Browse completed and active clinical studies to see how research communications are being automated and improved with Mosio.
Some studies where Mosio was used (mentioning us is appreciated, but not required). Contact us to add your study or make a correction.
An SMS Text Message–Based Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Program for Hispanic Adolescents With Obesity: Qualitative Co-Design Process
[2023]
Erica Soltero, PhD, Callie Lopez, BSc, Sandra Mihail, BSc, MPH, Ayleen Hernandez, BA, Salma M Musaad, MD, PhD, Teresia M O’Connor, MPH, MD, and Debbe Thompson, PhD
Objective:This study aimed to use a co-design process to inform the development of SMS text messages that promote healthy physical activity (PA) and sleep behaviors among Hispanic adolescents with obesity.
More Details
Skills to Enhance Positivity in adolescents at risk for suicide: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial
[2023]
Shirley Yen, Nazaret Suazo, Jackson Doerr, Natalia Macrynikola, Leanna S. Villarreal, Sophia Sodano, Kimberly H. M. O’Brien, Jennifer C. Wolff, Christopher Breault, Brandon E. Gibb, Rani Elwy, Christopher W. Kahler, Megan Ranney, Richard Jones, Anthony Spirito
Objective: To test the effectiveness of STEP, compared to Enhanced Treatment as Usual (ETAU), in reducing suicidal events and ideation in adolescents admitted to inpatient psychiatric care due to suicide risk. We hypothesize that those randomized to STEP, compared to ETAU, will have lower rates of suicide events, active suicidal ideation (SI), and depressed mood over the 6-month follow-up period. We hypothesize that those randomized to STEP, compared to ETAU, will demonstrate greater improvement in the hypothesized mechanisms of attention to positive affect stimuli and gratitude and satisfaction with life.
More Details
Two concurrent randomized controlled trials of CommunityRx, a social care intervention for family and friend caregivers delivered at the point of care
[2023]
Emily Marie Abramsohn, MariaDelSol De Ornelas, Soo Borson, Cristianne Rm Frazier, Charles M Fuller, Mellissa Grana, Elbert S Huang, Jyotsna S Jagai, Jennifer A Makelarski, Doriane Miller, Dena Schulman-Green, Eva Shiu, Katherine Thompson, Victoria Winslow, Kristen Wroblewski, Stacy Tessler Lindau
Background: CommunityRx is an evidence-based social care intervention delivered to family and friend caregivers (“caregivers”) at the point of healthcare to address health-related social risks (HRSRs). CommunityRx-Hunger is a double-blind randomized controlled trial (RCT) that enrolls caregivers of hospitalized children. CommunityRx-Dementia is a single-blind RCT that enrolls caregivers of community-residing people with dementia. Clinical trials that enroll caregivers face recruitment barriers, including caregiver burden and lack of systematic strategies to identify and track caregivers. COVID-19 pandemic-related visitor restrictions exacerbated these barriers and prompted the need for iteration of the CommunityRx protocols from in-person to remote operations. This study describes the novel methods used to iterate existing RCT protocols and factors contributing to their successful iteration.
More Details
Embedded emergency department physical therapy versus usual care for acute low back pain: a protocol for the NEED-PT randomised trial
[2022]
Howard S Kim, Kayla M Muschong, Ivy L Fishman,1 Jacob M Schauer, Amee L Seitz, Kyle J Strickland, Bruce L Lambert, Danielle M McCarthy, My H Vu, and Jody D Ciolino
Study Objective: Low back pain is a common problem and a substantial source of morbidity and disability worldwide. Patients frequently visit the emergency department (ED) for low back pain, but many experience persistent symptoms at 3 months despite frequent receipt of opioids. Although physical therapy interventions have been demonstrated to improve patient functioning in the outpatient setting, no randomised trial has yet to evaluate physical therapy in the ED setting.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | REDCap Integration | Alerts + Reminders
Implementing a mHealth intervention to increase colorectal cancer screening among high-risk cancer survivors treated with radiotherapy in the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS)
[2022]
Tara O. Henderson, Jenna K. Bardwell, Chaya S. Moskowitz, Aaron McDonald, Chris Vukadinovich, Helen Lam, Michael Curry, Kevin C. Oeffinger, Jennifer S. Ford, Elena B. Elkin, Paul C. Nathan, Gregory T. Armstrong, and Karen Kim
Study Objective: The ASPIRES study will assess the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and implementation of an intervention to increase the rate of CRC screening (colonoscopy and/or multitarget stool DNA test) among high-risk cancer survivors through interactive, educational text-messages and electronic resources provided to participants, and CRC screening resources provided to their primary care providers.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Pediatric Research Observing Trends and Exposures in COVID-19 Timelines (PROTECT): Protocol for a Multisite Longitudinal Cohort Study
[2022]
Burns J, Rivers P, LeClair LB, Jovel KS, Rai RP, Lowe AA, Edwards LJ, Khan SM, Mathenge C, Ferraris M, Kuntz JL, Lamberte JM, Hegmann KT, Odean MJ, McLeland-Wieser H, Beitel S, Odame-Bamfo L, Schaefer Solle N, Mak J, Phillips AL, Sokol BE, Hollister J, Ochoa JS, Grant L, Thiese MS, Jacoby KB, Lutrick K, Pubillones FA, Yoo YM, Rentz Hunt D, Ellingson K, Berry MC, Gerald JK, Lopez J, Gerald LB, Wesley MG, Krupp K, Herring MK, Madhivanan P, Caban-Martinez AJ, Tyner HL, Meece JK, Yoon SK, Fowlkes AL, Naleway AL, Gwynn L, Burgess JL, Thompson MG, Olsho LE, Gaglani M
Study Objective: This report describes the objectives and methods for conducting the Pediatric Research Observing Trends and Exposures in COVID-19 Timelines (PROTECT) study. PROTECT is a longitudinal prospective pediatric cohort study designed to estimate SARS-CoV-2 incidence and COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness (VE) against infection among children aged 6 months to 17 years, as well as differences in SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine response between children and adolescents.
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
A Brief Educational Intervention to Increase ED Initiation of Buprenorphine for Opioid Use Disorder (OUD)
[2022]
Utsha G. Khatri, Kathleen Lee, Theodore Lin, Joseph L. D’Orazio, Mitesh S. Patel, Frances S. Shofer, Jeanmarie Perrone
Study Objective: Despite the evidence in support of the use of buprenorphine in the treatment of OUD and increasing ability of emergency medicine (EM) clinicians to prescribe it, emergency department (ED)-initiated buprenorphine is uncommon. Many EM clinicians lack training on how to manage acute opioid withdrawal or initiate treatment with buprenorphine. We developed a brief buprenorphine training program and assessed the impact of the training on subsequent buprenorphine initiation and knowledge retention.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Crowdsourced Community Support Resources Among Patients Discharged From the Emergency Department During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Pilot Feasibility Study
[2022]
Anish K Agarwal, MD, MPH, MSHP, Lauren Southwick, MPH, Rachelle Schneider, MSW, Arthur Pelullo, MS, Robin Ortiz, MD, MSHP, Elissa V Klinger, MS, Rachel E Gonzales, BA, Roy Rosin, MBA, and Raina M Merchant, MD, MSPH1
Study Objective: Using an SMS text message-based system, we sought to build and test a remote model to explore community needs, connect individuals to curated resources, and facilitate community health worker intervention when needed during the pandemic. The primary aims of this pilot study were to establish the feasibility (ie, engagement with the text line) and acceptability (ie, participant ratings of resources and service) of delivering automated well-being resources via smartphone technology.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Mycophenolate Mofetil-Related Diarrhea and Beta-Glucuronidase Activity Following Kidney Transplantation
[2022]
Onyeaghala GC, Elmer S, Schladt D, Yang P, Wagner M, Teigen L, Al-Kofahi M, Wu B, Guan W, Staley C, Riad S, Matas A, Remmel R, Oetting W, Dorr CR, Jacobson P, Israni A.
Study Objective:The treatment of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)-related diarrhea in kidney transplants recipients often involves dose reductions, which may result in less effective immunosuppression. We hypothesize that bacterial beta-glucuronidase activity, which is a key enzyme in MMF enterohepatic recirculation, is associated with diarrhea occurrence.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Can We Eliminate Opioids After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction? A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial
[2021]
Vasilios Moutzouros 1, Toufic R Jildeh 1, Joseph S Tramer 1, Fabien Meta 1, Noah Kuhlmann 1, Austin Cross 1, Kelechi R Okoroha 2
Study Objective:To compare a multimodal nonopioid pain protocol versus traditional opioid medication for postoperative pain control in patients undergoing anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR).
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Infant with Clefts Observation Outcomes Instrument (iCOO): A New Outcome for Infants and Young Children with Orofacial Clefts
[2021]
Todd C Edwards 1, Carrie L Heike 1 2 3, Kathleen A Kapp-Simon 4 5, Salene M Jones 6, Brian G Leroux 1, Laura P Stueckle 2 3, Claudia Crilly Bellucci 4 5, Janine M Rosenberg 7, Meredith Albert 4 5, Cassandra L Aspinall 2 3, Donald L Patrick 1
Study Objective:We evaluated the measurement properties for item and domain scores of the Infant with Clefts Observation Outcomes Instrument (iCOO).
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Video-Counseling Intervention to Address HIV Care Engagement, Mental Health, and Substance Use Challenges: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial for Youth and Young Adults Living with HIV
[2021]
Parya Saberi, Caravella McCuistian, Emily Agnew, Angie R. Wootton, Dominique A. Legnitto Packard, Carol Dawson-Rose, Mallory O. Johnson, Valerie A. Gruber, and Torsten B. Neilands
Study Objective: Substance use and mental health are two barriers to engagement in care and antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence among youth and young adults living with HIV (YLWH). The consequences of suboptimal adherence in YLWH are increased risk of HIV transmission and a future generation of immunodeficient adults with drug-resistant virus.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Variability and change over time of weight and BMI among adolescents and adults with Prader-Willi syndrome: a 6-month text-based observational study
[2020]
Caroline J. Vrana-Diaz, Priya Balasubramanian, Nathalie Kayadjanian, Jessica Bohonowych, and Theresa V. Strong
Study Objective: Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder in which hyperphagia (excessive appetite) is a hallmark feature. Understanding how weight changes over time in this population is important for capturing the contemporary natural history of the disorder as well as assessing the impact of new treatments for hyperphagia. Therefore, we aimed to determine the feasibility of a remote assessment of weight change over time in PWS.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Protocol paper: Stepped wedge cluster randomized trial translating the ABCS into optimizing cardiovascular care for people living with HIV
[2020]
Stephen K. Williams, Brent A. Johnson, Jonathan N. Tobin, Amneris Esther Luque, Mechelle Sanders, Jennifer K. Carroll, Andrea Cassells, Tameir Holder, and Kevin Fiscella
Study Objective: People living with HIV (PWH) are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and stroke in comparison to their non-infected counterparts. The ABCS (aspirin-blood pressure control-cholesterol control-smoking cessation) reduce atherosclerotic (ASCVD) risk in the general population, but little is known regarding strategies for promoting the ABCS among PWH. Guided by the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR), we designed multilevel implementation strategies that target PWH and their clinicians to promote appropriate use of the ABCS based on a 10-year estimated ASCVD risk. Implementation strategies include patient coaching, automated texting, peer phone support, academic detailing and audit and feedback for the patient’s clinician. We are evaluating implementation through a stepped wedge cluster randomized trial based on the Reach-Effectiveness-Adoption-Maintenance/Qualitative-Evaluation-for-Systematic-Translation (RE-AIM/QuEST) mixed methods framework that integrates quantitative and qualitative assessments. The primary outcome is change in ASCVD risk. Findings will have important implications regarding strategies for reducing ASCVD risk among PWH.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Addressing HIV care, mental health and substance use among youth and young adults in the Bay Area: description of an intervention to improve information, motivation and behavioral skills
[2021]
Caravella McCuistian, Angie R Wootton, Dominique Legnitto-Packard, Valerie A. Gruber, Carol Dawson-Rose, Mallory O. Johnson, and Parya Saberi
Study Objective: Youth represent a population disparately impacted by the HIV epidemic. With most new HIV diagnoses occurring among adolescents and young adults, novel approaches to address this disparity are necessary. The objective of the current study was to describe the Youth to Telehealth and Text to Improve Engagement in Care (Y2TEC) intervention, which aims to fill this gap. The Y2TEC intervention (trial registration NCT03681145) offers an innovative approach to improve HIV treatment engagement among youth living with HIV by focusing on treatment barriers related to mental health and substance use. This allows for a holistic approach to providing culturally informed intervention strategies for this population. More Details and More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Improving Mood Through Community Connection and Resources Using an Interactive Digital Platform: Development and Usability Study
[2021]
Robin Ortiz, MD, Lauren Southwick, MPH, Rachelle Schneider, Elissa V Klinger, MS, Arthur Pelullo, MS, Sharath Chandra Guntuku, PhD, Raina M Merchant, MD, and Anish K Agarwal, MD, MPH
Study Objective: This study aimed to prospectively investigate the ability of a health system–based digital, remote, interactive tool to provide health and well-being resources to local community participants and to foster connectivity among them during the early phases of COVID-19. More Details and More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Gamified Text Messaging Contingent on Device-Measured Steps: Randomized Feasibility Study of a Physical Activity Intervention for Cancer Survivors
[2020]
Michael C Robertson, Elizabeth J Lyons, Yue Liao, Miranda L Baum, Karen M Basen-Engquist
Study Objective: The primary aim of this study is to evaluate the feasibility and acceptability of Steps2Health, a physical activity intervention for cancer survivors. It also aims to investigate the effects of the intervention on motivation, physical activity, and step count. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Optimization of an mHealth lifestyle intervention for families with hereditary cancer syndromes: Study protocol for a multiphase optimization strategy feasibility study
[2022]
Karen Basen-Engquist, Margaret Raber, Larkin L.Strong, Susan Schembre, Liang Li Banu Arun, Karen Lu, Nancy You, Eduardo Vilar, Patrick Lynch, Sara Fares, Susan K. Peterson
Study Objective: Individuals at increased hereditary risk of cancer are an important target for health promotion and cancer prevention interventions. Health-4-Families uses the Multiphase Optimization STrategy (MOST) framework and is designed to pilot digital delivery strategies for a distance-based, 16-week intervention to promote weight management, healthy diet, and increased physical activity among individuals with BRCA1/BRCA2 or DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathogenic germline variants. This communication describes participant recruitment and the design of the Health-4-Families pilot study. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Patient-Reported Opioid Consumption and Pain Intensity After Common Orthopedic and Urologic Surgical Procedures With Use of an Automated Text Messaging System
[2021]
Anish K. Agarwal, MD, MPH, MS, Daniel Lee, MD, MS, […], and M. Kit Delgado, MD, MS
Study Objective: To assess the difference between the number of opioid tablets prescribed and the self-reported number of tablets taken as well as self-reported pain intensity and ability to manage pain after orthopedic and urologic procedures with use of an automated text messaging system. More Details and More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Age Significantly Affects Response Rate to Outcomes Questionnaires Using Mobile Messaging Software
[2021]
Toufic R. Jildeh, M.D., Joshua P. Castle, M.D., […], and Kelechi R. Okoroha, M.D.
Study Objective: To investigate the demographic factors that influence time to respond (TTR), time to completion (TTC), and response rate when using a text messaging-based system and to determine the feasibility and applicability of mobile messaging-based services for collection of patient-reported outcomes among orthopedic sports medicine patients. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Reach out behavioral intervention for hypertension initiated in the emergency department connecting multiple health systems: study protocol for a randomized control trial
[2020]
William J. Meurer, corresponding author, Mackenzie Dinh,1 Kelley M. Kidwell, Adam Flood, Emily Champoux, Candace Whitfield, Deborah Trimble,1 Joan Cowdery, Dominic Borgialli, Sacha Montas, Rebecca Cunningham, Lorraine R. Buis, Devin Brown, and Lesli Skolarus
Study Objective: Hypertension is the most important modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of mortality in the United States. The Emergency Department represents an underutilized opportunity to impact difficult-to-reach populations. There are 136 million visits to the Emergency Department each year and nearly all have at least one blood pressure measured and recorded. Additionally, an increasing number of African Americans and socioeconomically disadvantaged patients are overrepresented in the Emergency Department patient population. In the age of electronic health records and mobile health, the Emergency Department has the potential to become an integral partner in chronic disease management. The electronic health records in conjunction with mobile health behavior interventions can be leveraged to identify hypertensive patients to impact otherwise unreached populations. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Use of a Long-Acting Opioid Microsphere Formulation to Overcome Difficulties in Swallowing Pain Medication
[2020]
Nathan Anderson, Andrea G Gillman, and Ajay D Wasan
Study Objective: To achieve optimal care for pain patients, pain medication should provide satisfactory analgesia and minimize patient burdens such as the effort required to swallow pills. Although there are risks of abuse, overdose, and side effects,1 long-term low- or moderate-dose opioid medication can provide effective and safe analgesia in well-selected patients with chronic pain. However, long-acting opioid pill capsules are often large and difficult for patients to swallow.2 Studies have shown that 20% of adult patients have difficulty swallowing their medications, and up to 10% refuse specific pharmaceutical therapies because they cannot swallow the pills.3,4 Pill swallowing difficulty can be due to several factors, including capsule size, outer coating texture, shape, and taste,5,6 and it is likely that swallowing difficulties compromise the quantity, quality, and satisfaction with pain relief from oral opioids. This issue disproportionately affects patients with cancer pain, as chemotherapy, radiation, and/or surgical treatments may result in increased swallowing difficulties. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Moving Antiretroviral Adherence Assessments to the Modern Era: Correlations Among Three Novel Measures of Adherence
[2020]Parya Saberi, Deepalika Chakravarty, Kristin Ming, Dominique Legnitto, Monica Gandhi, Mallory O. Johnson, and Torsten B. Neilands
Study Objective: There is no gold standard for estimating antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence. Feasible, acceptable, and objective measures that are cost- and time-effective are needed. US adults (N = 93) on ART for ≥ 3 months, having access to a mobile phone and internet, and willing to mail in self-collected hair samples, were recruited into a pilot study of remote adherence data collection methods. We examined the correlation of self-reported adherence and three objective remotely collected adherence measures: text-messaged photographs of pharmacy refill dates for pharmacy-refill-based adherence, text-messaged photographs of pills for pill-count-based adherence, and assays of home-collected hair samples for pharmacologic-based adherence. All measures were positively correlated. The strongest correlation was between pill-count- and pharmacy-refill-based adherence (r = 0.68; p < 0.001), and the weakest correlation was between self-reported adherence and hair drug concentrations (r = 0.14, p = 0.34). The three measures provide objective adherence data, are easy to collect, and are viable candidates for future HIV treatment and prevention research. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Feasibility of Text Messaging to Augment Brief Advice and Nicotine Replacement Therapy for Smoking Cessation in College Students
[2019]
Deepa R Camenga, Steven L. Bernstein, James Dziura, Lynn Fiellin, and Suchitra Krishnan-Sarinc
Study Objective: To test the feasibility of a university health center-delivered smoking cessation intervention that adds a 6–week course of text messaging to brief advice and nicotine patch therapy.
Overcoming Technological Challenges: Lessons Learned from a Telehealth Counseling Study
[2019]
Angie R. Wootton, Caravella McCuistian, Dominique A. Legnitto Packard, Valerie A. Gruber, and Parya Saberi
Study Objective: Telehealth methods, including video chat counseling, have been growing in popularity within the behavioral health counseling field for over a decade. While video-based counseling methods have been shown to be effective and convenient, they have unique challenges stemming from the technology they use. Technical challenges can negatively impact appointment flow, intervention effectiveness, and the satisfaction of both patients and clinicians. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Feasibility of text messaging to promote child health in a rural community on an American Indian reservation
[2019]
Blakely Brown, Kari Harris, Laura Dybdal, Julia Malich, Brenda Bodnar, Emily Hall
Study Objective: This study investigated the feasibility of delivering health-related short text messages to parents with the goal of reducing obesity risk among their children aged 3–5 years.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Pilot study to inform young adults about the risks of electronic cigarettes through text messaging
[2019]
Karen S. Calabro, Georges E. Khalil, Minxing Chen, Cheryl L. Perry, and Alexander V. Prokhorov
Study Objective: Young adults are rapidly adopting electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) use. The popularity of e-cigarettes among young people can be attributed to heavy industry advertising and misleading health claims. Data indicate that young e-cigarette users who have never used conventional cigarettes may transition toward smoking combustible cigarettes. Communicating e-cigarette risks via text messaging is limited. This pilot study assessed the impact of exposure to 16 text messages on e-cigarette knowledge and risk perception. The short text messages delivered to participants conveyed e-cigarette use may lead to addiction to nicotine and explained the latest health-related findings. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Using a Web-Based Data Collection Platform to Implement an Effective Electronic Patient-Reported Outcome Registry
[2019]
Vincent A. Lizzio, M.D., Caleb M. Gulledge, B.S., Fabien Meta, M.D., Sreten Franovic, B.S., M.S., and Eric C. Makhni, M.D., M.B.A
Study Objective: Modern health care places significant emphasis on patient-centered care. As a result, many orthopedic providers are incorporating routine patient-reported outcome measure (PROM) collection into their practice. However, routine PROM collection often disrupts clinical workflow and can place a burden on both the patient and the provider. Electronic PROM collection systems, if implemented deliberately to maximize convenience and efficiency, have the potential to mitigate these obstacles. This technique guide presents an overview of designing and implementing a PROM-based clinical registry for the ambulatory orthopedic clinic using Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap; Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN). We outline the basic steps of creating a simple but effective patient registry using this accessible data collection platform. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat | REDCap Integration
Small, But Mighty: How a Rare Disease Foundation Built Natural History Data to Accelerate New Therapies
[2018]
Theresa Strong and Team
Summary: The Foundation for Prader-Willi Research was established with one aim in mind: to eliminate the challenges of Prader-Willi syndrome, or PWS, through the advancement of research and therapeutic development. But it’s not always easy given the lack of natural history data on the condition, which only affects one in every 15,000 people. Here is how the Foundation used CTTI’s Digital Health Trials recommendations to successfully establish baseline data for weight changes in PWS patients to support sponsors of PWS research in designing more impactful trials. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Telehealth and texting intervention to improve HIV care engagement, mental health and substance use outcomes in youth living with HIV: a pilot feasibility and acceptability study protocol
[2018]
Angie R Wootton, Dominique A Legnitto, Valerie A Gruber, Carol Dawson-Rose, Torsten B Neilands, Mallory O Johnson, Parya Saberi
Study Objective: The Y2TEC study is a single-site randomised pilot study with the primary aim of examining the feasibility and acceptability of a 12-session telehealth and text message–based counselling series for YLWH. The secondary aim is to evaluate the preliminary impact of the intervention on improved engagement in HIV care, enhanced mental health and reduced substance use for YLWH. The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) Institutional Review Board (IRB) has reviewed and approved this study. The intervention was designed based on the results of our formative mixed-methods and qualitative research on youth-friendly HIV counselling methods. The intervention is delivered to participants in two condition groups (ie, intervention and waitlist control) via remote telehealth sessions delivered over 4 months, with a cross-over design (see table 1). The overall duration of participation is 8 months. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Appointment Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Being Present: A single-arm feasibility study of audio-based mindfulness meditation for colorectal cancer patients and caregivers
[2018]
Chloe E. Atreya, Ai Kubo, Hala T. Borno, Blake Rosenthal, Matthew Campanella, John P. Rettger, Galen Joseph, I. Elaine Allen, Alan P. Venook, Andrea Altschuler, Anand Dhruva
Study Objective: A metastatic cancer diagnosis is associated with high levels of distress in patients and caregivers. Mindfulness interventions can reduce distress and improve quality of life in cancer patients. However, standard mindfulness training relies on in-person instruction, which is often not practical for either patients receiving chemotherapy or their caregivers. In the Being Present single arm pilot study, we designed and tested an 8-week audio-based mindfulness meditation program for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy with or without a participating caregiver. The study accrued 33 of 74 (45%) eligible patients consenting together with 20 family caregivers (53 participants total) within nine months. Forty-one participants were evaluable (77%); 10 of 12 cases of attrition were attributable to hospitalization or death. Median participant age was 51 (range 21–78 years); 38% were men. Baseline levels of distress were similar in patients and caregivers. The top reasons for participation cited in pre-intervention interviews were to increase relaxation/calm, improve mood/emotions, and reduce stress/anxiety. In measures of adherence, 59% of responses to weekly texts asking: “Have you practiced today?” were “Yes” and 59% of interviewees reported practicing >50% of the time. Compared to baseline, post-intervention surveys demonstrated significantly reduced distress (p = 0.01) and anxiety (p = 0.03); as well as increased non-reactivity (p<0.01), and feeling at peace (p<0.01). Post-intervention qualitative interviews, where 71% of participants reported benefit, were consistent with quantitative findings. In the interviews, participants spontaneously described reduced stress/anxiety and increased relaxation/calm. Benefits appeared to be accentuated in patient-caregiver pairs as compared to unpaired patients. Seventy-nine percent of participants reported plans for continued practice after study completion. We conclude that the Being Present audio-based mindfulness meditation program is of interest to, feasible, and acceptable for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and caregivers, with initial evidence of efficacy. These results will guide plans for a follow-up study. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Novel methods to estimate antiretroviral adherence: protocol for a longitudinal study
[2018]
Parya Saberi, Kristin Ming, Dominique Legnitto, Torsten B Neilands, Monica Gandhi, and Mallory O Johnson
Study Objective: There is currently no gold standard for assessing antiretroviral (ARV) adherence, so researchers often resort to the most feasible and cost-effective methods possible (eg, self-report), which may be biased or inaccurate. The goal of our study was to evaluate the feasibility and acceptability of innovative and remote methods to estimate ARV adherence, which can potentially be conducted with less time and financial resources in a wide range of clinic and research settings. Here, we describe the research protocol for studying these novel methods and some lessons learned. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Pilot Study of Triphala and Rubia Cordifolia on Gut Microbiome and Skin
[2018]
Raja Sivamani, MD, University of California-Davis, Department of Dermatology
Study Objective: Herbal supplements such as Rubia cordifolia and Triphala [a mix of Emblica officinalis (Amalaki), Terminalia bellerica (Bibhitaki), and Terminalia chebula (Haritaki)] are commonly used for skin based treatments in India. However, the scientific evidence for their specific effects on the skin are scant. Rubia cordifolia is a root that is used in skin care for pigmentation and inflammation.1 Triphala is thought to have antioxidant properties and reduce inflammation in general. Herbs have been shown to modulate the gut microbiome, as previous studies have suggested that triphala may modify the gut microbiome. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Pilot Randomized Trial of an Automated Smoking Cessation Intervention via Mobile Phone Text Messages as an Adjunct to Varenicline in Primary Care
[2018]
Jessica M. Yingst, Susan Veldheer, Shari Hrabovsky, Erin Hammett, James Nicholson, Arthur Berg & Jonathan Foulds
Study Objective: Varenicline is a safe and effective aid to smoking cessation but most trials have involved frequent visits or intensive behavioral support unlike that typically provided in primary care. The current study examined if motivational text messages, sent via cellphone, would increase quit rates in smokers being treated with varenicline and 3 brief sessions in a family practice setting. Methods: This study was a randomized controlled, parallel-group smoking cessation trial. Intervention group participants (n = 74) received daily motivational text messages, additional texted tips in response to keywords, and weekly study questions while control group participants (n = 76) received only weekly study questions. Both groups received individualized counseling. Self-reported non-smoking and exhaled breath CO <10ppm were used to validate smoking abstinence at 3 weeks and 12 weeks. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Use of Xtampza ER to overcome difficulties in swallowing opioid pills
[2017]
Ajay Wasan, MD, MSc, Andrea G. Gillman, PhD
Study Objective: Xtampza ER is an oral opioid medication capsule that can be opened to allow the pellets to be added to food or drink. This study will investigate whether Xtampza ER can adequately address common quality of care deficits of opioid medications. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Appointment Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Reach Out Churches: A Community-Based Participatory Research Pilot Trial to Assess the Feasibility of a Mobile Health Technology Intervention to Reduce Blood Pressure Among African Americans
[2017]
Lesli E. Skolarus, MD, MS, Joan Cowdery, PhD, Mackenzie Dome, MS, Sarah Bailey, MA, Jonggyu Baek, PhD, James Brian Byrd, MD, MS, Sarah E. Hartley, MD, Staci C. Valley, MD, Sima Saberi, MD, Natalie C. Wheeler, MD, Mollie McDermott, MD, Rebecca Hughes, BA, Krithika Shanmugasundaram, BS, Lewis B. Morgenstern, MD, Devin L. Brown, MD, MS
Study Objective: Innovative strategies are needed to reduce the hypertension epidemic among African Americans. Reach Out was a faith-collaborative, mobile health, randomized, pilot intervention trial of four mobile health components to reduce high blood pressure (BP) compared to usual care. It was designed and tested within a community-based participatory research framework among African Americans recruited and randomized from churches in Flint, Michigan.
More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Edtech-HPV: A Community Approach Using Education and Technology to Increase HPV Vaccination (Edtech-HPV)
[2017]
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Study Objective: This study is a two-arm randomized controlled trial, implemented to assess the effectiveness of a community-based educational program with and without a text messaging reminder system, in increasing the rate of HPV vaccination completion among children of Mexican Americans. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Facet joint injections for people with persistent non-specific low back pain (Facet Injection Study): a feasibility study for a randomized controlled trial
[2017]
David R Ellard, Martin Underwood, Felix Achana, James HL Antrobus, Shyam Balasubramanian, Sally Brown, Melinda Cairns, James Griffin, Frances Griffiths, Kirstie Haywood, Charles Hutchinson, Ranjit Lall, Stavros Petrou, Nigel Stallard, Colin Tysall, David A Walsh, Harbinder Sandhu
Study Objective: Mosio provided text messaging services for the collection of daily/weekly pain scores from participants. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Appointment Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Feasibility and Acceptability of Text Messaging to Assess Daily Substance Use and Sexual Behaviors among Urban Emerging Adults
[2017]
Erin E. Bonar, Rebecca M. Cunningham, R. Lorraine Collins, James A. Cranford, Stephen T. Chermack, Marc A. Zimmerman, Frederic C. Blow, and Maureen A. Walton
Study Objective: Daily process research can help distinguish causal relationships between substance use and sexual risk behaviors in high-risk groups, such as urban emerging adults. We employed text messaging to assess 18–25 year-olds’ daily substance use and sexual risk behaviors over 28 days. We describe the implementation of this method, attitudes regarding the daily surveys, and correlates of survey completion. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Advice given by community members to pregnant women: a mixed methods study
[2016]
Bianca A. Verma, Lauren P. Nichols, Melissa A. Plegue, Michelle H. Moniz, Manisha Rai, and Tammy Chang
Study Objective: Smoking and excess weight gain during pregnancy have been shown to have serious health consequences for both mothers and their infants. Advice from friends and family on these topics influences pregnant women’s behaviors. The purpose of our study was to compare the advice that community members give pregnant women about smoking versus the advice they give about pregnancy weight gain. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Developing predictive models for return to work using the Military Power, Performance and Prevention (MP3) musculoskeletal injury risk algorithm: a study protocol for an injury risk assessment program
[2016]
Daniel I Rhon, Deydre S Teyhen, Scott W Shaffer, Stephen L Goffar, Kyle Kiesel, and Phil P Plisky
Study Objective: Musculoskeletal injuries are a primary source of disability in the US Military, and low back pain and lower extremity injuries account for over 44% of limited work days annually. History of prior musculoskeletal injury increases the risk for future injury. This study aims to determine the risk of injury after returning to work from a previous injury. The objective is to identify criteria that can help predict likelihood for future injury or re-injury. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Randomized Controlled Trial Examining Health Care Access Interventions for Taxi Drivers
[2016]
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Study Objective: The purpose of this study is to compare the effectiveness of providing the usual health fair service and follow-up alone plus additional interventions of Navigation Case Management (NCM) or mobile text messaging (mTECH) and Taxi health Improvement Promoter (TIP). The addition of NCM or mTECH and TIP to the usual follow-up could prove to be more effective in finding the best way to make sure taxi drivers go to important medical appointments and have a regular doctor to help with their health problems. This study will help researchers find out whether the different approaches are better, the same as, or worse than the usual approach. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Appointment Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
HIV Disclosure and Transmission Risks to Sex Partners Among HIV-Positive Men
[2016]
Seth C. Kalichman, PhD, corresponding author Moira O. Kalichman, MSW, Chauncey Cherry, PhD, and Tamar Grebler, BA
Study Objective: Disclosure of HIV-positive status to sex partners is critical to protecting uninfected partners. In addition, people living with HIV often risk criminal prosecution when they do not inform sex partners of their HIV status. The current study examined factors associated with nondisclosure of HIV status by men living with HIV in Atlanta, GA (92% African African, mean age = 43.8), who engage in condomless sex with uninfected sex partners. Sexually active HIV-positive men (N = 538) completed daily electronic sexual behavior assessments over the course of 28 days and completed computerized interviews, drug testing, medication adherence assessments, and HIV viral load retrieved from medical records. Results showed that 166 (30%) men had engaged in condomless vaginal or anal intercourse with an HIV-uninfected or unknown HIV status sex partner to whom they had not disclosed their HIV status. Men who engaged in non-disclosed condomless sex were less adherent to their HIV treatment, more likely to have unsuppressed HIV, demonstrated poorer disclosure self-efficacy, enacted fewer risk reduction communication skills, and held more beliefs that people with HIV are less infectious when treated with antiretroviral therapy. We conclude that undisclosed HIV status is common and related to condomless sex with uninfected partners. Men who engage in non-disclosed condomless sex may also be more infectious given their nonadherence and viral load. Interventions are needed in HIV treatment as prevention contexts that attend to disclosure laws and enhance disclosure self-efficacy, improve risk reduction communication skills, and increase understanding of HIV infectiousness. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Sexual Behaviors and Transmission Risks among People Living with HIV: Beliefs, Perceptions, and Challenges to Using Treatments as Prevention
[2015]
Seth C. Kalichman, Chauncey Cherry, Moira O. Kalichman, Christopher Washington, Tamar Grebler, Ginger Hoyt, Cindy Merely, and Brandi Welles
Study Objective: Antiretroviral therapy (ART) improves the health of people living with HIV and can reduce infectiousness, preventing HIV transmission. The potential preventive benefits of ART are undermined by beliefs that it is safe to have condomless sex when viral load is below levels of detection (infectiousness beliefs and risk perceptions). In this study we hypothesized that infectiousness beliefs and HIV transmission risk perceptions would prospectively predict people living with HIV engaging in more condomless sex with HIV-negative and unknown HIV status sex partners. Sexually active HIV-positive men (n=538, 76%) and women (n= 166, 24%) completed computerized interviews of sexually transmitted infections (STI) symptoms and diagnoses, unannounced pill counts for medication adherence, medical chart abstracted HIV viral load, and 28 daily cell-phone delivered prospective sexual behavior assessments. Results showed that a total of 313 (44%) participants had engaged in condomless sex with HIV-negative/unknown status sex partners and these individuals demonstrated higher rates of STI symptoms and diagnoses. Two-thirds of participants who had condomless sex with HIV-negative/unknown status partners had not disclosed their HIV status. Multivariable logistic regression models showed that beliefs regarding viral load and HIV infectiousness and perceptions of lower risk for HIV transmission resulting from HIV viral suppression predicted condomless sex with potentially uninfected partners over and above sex behaviors with HIV-positive partners and STI symptoms/diagnoses. Interventions that address HIV status disclosure and aggressively treat STI in sexually active people living with HIV should routinely accompany the use of HIV treatments as prevention. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Wraparound care for youth injured by violence: study protocol for a pilot randomized control trial
[2015]
Carolyn Snider, Depeng Jiang, Sarvesh Logsetty, Trevor Strome, and Terry Klassen
Study Objective: Injury by violence is the fourth cause of death and the leading reason for a youth to visit an emergency department (ED) in Canada. In Winnipeg, 20% of youth who visit an ED with an injury due to violence have a second visit for a subsequent violent injury within 1 year. Youth injured by violence are in a reflective and receptive state of mind, rendering the ED setting appropriate for intervention. More Details
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Storylines | Alerts + Reminders
Text Message Appointment Reminders Increase Patient Engagement in Clinical Trials (Case Study)
[2015]
IQVIA (formerly, Quintiles)
Key Findings:
- The amount of daily SMSs sent is positively correlated with study visit attendance rates.
- 175 average text messages sent per day is statistically associated with a 10.07% average increase in study visit attendance.
- There was a 91.6% reduction in resources utilized to remind study patients of screening visits.
- Increased ability to optimize study screening department planning and resources due to appointment confirmations.
Mosio Modules Used: Alerts + Reminders | Appointment Reminders | Interactive Text Chat
Text Messaging Enhances Clinical Trial Patient Recruitment (Case Study)
[2014]
Johnson County Clin-Trials (JCCT)
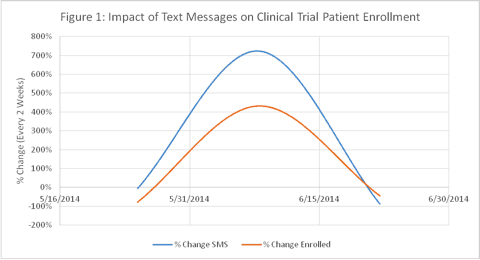
Figure 1 confirms that the increase in text messages also increased enrollment rates.
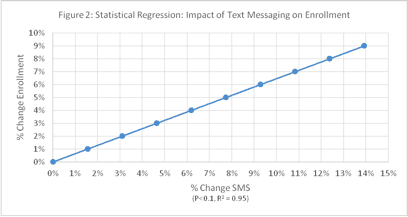
Figure 2 verifies that there was a statistically significant relationship between text messaging and patients enrolled.
Mosio Modules Used: Surveys | Alerts + Reminders | Appointment Reminders | Interactive Text Chat